Buy DSIP Peptide France
DSIP, or Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide, is a naturally occurring neuropeptide that plays a role in the regulation of sleep and various physiological processes. It is primarily known for its ability to induce and enhance deep sleep, also known as delta wave sleep.
Shop our Full Range of DSIP Peptides
-

BULK BUY
DSIP Peptide Vial
£20.99 – £178.47Price range: £20.99 through £178.47 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

DSIP Nasal Spray
£26.24 – £47.48Price range: £26.24 through £47.48 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

DSIP Pre-Mixed Pen 5mg
£38.84 – £104.86Price range: £38.84 through £104.86 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!
DSIP Epithalon Peptide Stack
£22.59 – £40.25Price range: £22.59 through £40.25 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 NEW
NEWEpithalon DSIP Nasal Stack
£43.19 – £77.38Price range: £43.19 through £77.38 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
What Is DSIP?
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide (DSIP) is a naturally occurring neuropeptide that has been closely linked to the regulation of sleep and various physiological processes. Discovered in the 1970s, DSIP is found in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain and plasma, and its key role lies in modulating sleep patterns. In particular, the induction and maintenance of delta wave sleep, or deep sleep.
It is believed to interact with several areas of the central nervous system, including the hypothalamus, where it influences human circadian rhythms and the initiation of sleep. France Researchers have also found that it might play a role in other regulatory processes, such as boosting mitochondrial function and modulating the secretion of hormones like growth hormone and cortisol, which are critical for overall bodily function.
Studies have examined its effects on chronic insomnia, major depression, immune function, and stress regulation, highlighting its role in overall health [1]. Available in various forms, including lyophilized preparations, DSIP France remains a focus of ongoing research, particularly through placebo-controlled studies. This peptide offers valuable insights into sleep disorders and central nervous system functions, making it a promising area of medical research.
DSIP Mechanism Of Action
The mechanism of action of Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide is still not fully understood, but research suggests it interacts directly with the central nervous system to regulate crucial processes.
It is thought to influence the sleep-wake cycle by affecting neurotransmitter activity, including that of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and serotonin. Additionally, it appears to help balance the release of hormones such as adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and luteinizing hormone, which are essential for stress response and reproduction. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier further supports its role in modulating brain activity.
Although much about the peptide is still being studied, its role in brain chemistry and hormone regulation makes it an important area of research for understanding sleep and stress-related conditions.
Source: PubChem
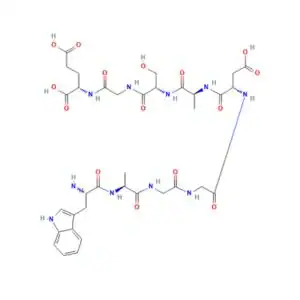
Structure of DSIP
Sequence: Trp-Ala Gly Gly AspAla-Ser-Gly-Glu
Molecular Formula: C35H48N10O15
Molecular Weight: 848.824
PubChem CID: 3623358
Research Benefits of Sleep With DSIP
Scientists have long been interested in Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide due to its potential effects on sleep patterns and overall sleep quality. Below are some key areas of study regarding it’s role in sleep research.
Sleep Latency
One of the main focuses of Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide research is its potential to reduce sleep latency—the time it takes to fall asleep. France Studies suggest that it may promote quicker relaxation, potentially shortening the time between going to bed and entering the first stage of sleep [2].
Slow-Wave Sleep
It is also being researched for its influence on slow-wave sleep, the deepest phase of non-REM sleep. Slow-wave sleep is vital for physical recovery and proper brain function. France Researchers are examining whether the peptide can enhance this stage, improving restorative processes during sleep [3].
Circadian Rhythm Regulation
DSIP France may play a role in regulating the body’s natural circadian rhythm, which governs sleep-wake cycles [4]. Researchers are investigating how Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide could help synchronize these rhythms, especially in those with disrupted sleep patterns caused by factors like shift work or jet lag.
Stress and Sleep Quality
High levels of stress can severely affect sleep efficiency. The potential calming effects of the compound are being explored to see if it can mitigate stress thereby improving overall sleep duration and restfulness.
It continues to be a molecule of interest in sleep research, offering promising insights into improving sleep quality and understanding biological recovery processes.
Other Potential Research Benefits
Reduces Stress and Anxiety: By modulating neurotransmitters like GABA and serotonin, DSIP helps to ease stress and lower anxiety levels, contributing to overall mental well-being [5].
Balances Hormone Levels: Research suggests it aids in regulating the release of hormones such as ACTH, helping the body manage stress and maintain reproductive health [6].
Supports Chronic Pain Relief: France Research indicates that it may help reduce pain sensitivity, making it useful for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions [7].
Enhances Cognitive Clarity: Some France studies suggest the peptide may boost mental clarity and cognitive performance, aiding memory and focus [8].
Potential Therapeutic Benefit in Stroke Recovery: A study demonstrated that Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide might have potential therapeutic benefits in stroke therapy, specifically in accelerating the recovery of motor functions after a stroke [9].
Supports Addiction Recovery: It is being studied for its role in managing withdrawal symptoms and aiding recovery in cases of alcohol and drug dependency [10].
Potential Role in Cancer Therapy: France Studies show promise in easing chemotherapy-related side effects and enhancing overall patient comfort during cancer treatments [11].
Improves Cardiovascular Health: France Research suggests it may help lower blood pressure and reduce oxidative stress and heart disease risk by promoting relaxation and stress relief [12].
Assists with Diabetes Management: By possibly influencing hormonal balance, it may support better regulation of blood sugar levels [13].
Promotes Emotional Stability: Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide may play a role in reducing depression symptoms, offering hope for those with mood-related disorders [14].
Buy DSIP Peptide France for research online today.
Buy DSIP Epithalon Peptide Vial Stack
Buy DSIP Epithalon peptide stack France for potential benefits to enhance research potential. Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide may aid relaxation, sleep regulation, and studies on stress management and circadian rhythm. Epithalon is being studied for its potential anti-ageing effects, including supporting telomere length and cellular health.
Together, this stack provides synergistic effects, making it a versatile tool for exploring ageing, wellness, and biological processes tied to sleep and recovery. Combining their benefits allows researchers to better understand their mechanisms and applications. Buy DSIP Epithalon peptide stack from Direct Peptides online today.
Buy DSIP Peptide Nasal Spray
Buy DSIP nasal spray France, it delivers Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide through the nasal passage for efficient absorption. This convenient system supports research on it’s potential benefits for sleep and relaxation.
Researchers study how it may help regulate sleep cycles, manage stress, and promote relaxation. The easy-to-use nasal spray format offers a practical option for exploring its effects. Its potential to influence circadian rhythms and aid recovery makes it valuable in peptide research. Buy DSIP nasal spray online, available in 15 ml and 30 ml glass spray bottles here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about DSIP
How does DSIP work?
It is believed to work by influencing various regions of the brain associated with sleep and hormonal balance. It interacts with the central nervous system and may modulate the release of key hormones like cortisol and melatonin.
Is DSIP administration safe for long-term use?
The long-term safety of this peptide for chronic insomnia is unclear due to limited trials. Patients should be cautious, as its prolonged effects are not well-studied. More research is needed to understand its long-term impact on nighttime symptoms.
Is DSIP safe to use?
It is generally considered safe for research purposes when used as intended within a controlled environment. However, any application beyond research should be approached with caution. It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional, as potential effects and outcomes can vary depending on individual circumstances.
Is DSIP legal?
The legal status depends on the country and its regulations. In the U.S., the FDA has not approved it for medical use and classifies it as a research chemical for scientific studies. In other regions, its use may be restricted or unregulated. Anyone interested should check local laws and consult authorities to ensure compliance.
How is DSIP administered?
It is available in several forms, including injectable vials, nasal sprays, and pre-mixed peptide pens. The method of administration varies depending on the product type and its intended research or investigational purpose. Injectable vials are supplied as a lyophilized powder that must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water before use.
Where can I buy DSIP?
Buy DSIP from reputable suppliers like Direct Peptides, known for providing 99% pure formulations. Available in various sizes and delivery options to meet diverse research needs. Enjoy the convenience of worldwide shipping.
Does DSIP require a prescription?
Since it is primarily marketed for research purposes, it may not require a prescription. However, regulations vary by region, so checking local laws and consulting a professional is advised.
Can DSIP be used alongside other peptides?
Yes, it is commonly included in peptide stacks to maximise its effects. Direct Peptides offers it in a peptide stack with Epithalon for enhanced research outcomes.
What are the potential side effects of DSIP?
While adverse effects are rare, possible side effects can include mild headaches, dizziness, or fatigue in some cases. Always follow guidelines for safe handling and consult a professional if concerns arise.
Buy DSIP Peptide Vial France in lyophilized form from Direct Peptides. Available in 2mg, 5mg and 10mg vials. High purity vials are also available in a convenient kit with bacteriostatic water for reconstitution.
Summary of Research Applications
- Enhances Sleep Quality
- Alleviates Chronic Pain
- Relieves Stress
- Enhances Cognitive Function
- Potential treatment for stroke patients
- Helps Combat Depression
- Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease
- Lowers Blood Pressure
- Aids in Cancer Prevention and Eases Chemotherapy Side Effects
- Manages Diabetes Symptoms
- Supports Recovery from Alcohol and Drug Addiction
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide Quality Assured
At Direct Peptides, we offer high-quality DSIP (Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide) products with 99% purity, produced under strict synthesis guidelines. Rigorous quality control ensures reliable, consistent batches.
Designed for various research purposes, our commitment to excellence ensures all our products meet high safety standards. Researchers can trust in the purity and consistency needed for advances in sleep and recovery studies, enabling accurate experiments and dependable results.
References For Further Reading
[1] M V Graf and A J Kastin (1984) Delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP): a review – Neuroscience Biobehavioural Reviews, 1984 Spring, Volume 8 (Issue 1), Pages 83-93.
[2] F Bes, W Hofman, J Schuur, and C Van Boxtel (1992) Effects of delta sleep-inducing peptide on sleep of chronic insomniac patients. A double-blind study – Neuropsychobiology, 1992, Volume 26 (Issue 4), Pages 193-7.
[3] V Susić, G Masirević, and S Totić (1987) The effects of delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) on wakefulness and sleep patterns in the cat – Brain Research, 1987 Jun 30, Volume 414 (Issue 2), Pages 262-70.
[4] M Graf, H Christen, H J Tobler, P F Maier, and G A Schoenenberger (1981) Effects of repeated DSIP and DSIP-P administration on the circadian locomotor activity of rats – Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behaviour, 1981 Nov, Volume 15 (Issue 5), Pages 717-21.
[5] M V Graf, A J Kastin, D H Coy, and A J Fischman (1985) Delta-sleep-inducing peptide reduces CRF-induced corticosterone release – Neuroendocrinology, 1985 Oct, Volume 41 (Issue 4), Pages 353-6.
[6] K V Sudakov, P E Umriukhin, E V Koplik, and K V Anokhin (2001) Delta-sleep inducing peptide (DSIP) and ACTH (4-10) analogue influence fos-induction in the limbic structures of the rat brain under emotional stress – Stress, 2001 Jun, Volume 4 (Issue 2), Pages 143-53.
[7] W Larbig, W D Gerber, M Kluck, and G A Schoenenberger (1984) Therapeutic effects of delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) in patients with chronic, pronounced pain episodes. A clinical pilot study – European Neurology, 1984, Volume 23 (Issue 5), Pages 372-85.
[8] Koustav Roy, Garima Chauhan, Punita Kumari, Meetu Wadhwa, et al (2018) Phosphorylated delta sleep inducing peptide restores spatial memory and p-CREB expression by improving sleep architecture at high altitude – Life Sciences, Volume 209, 15 September 2018, Pages 282-290.
[9] Elena A Tukhovskaya, Alina M Ismailova, Elvira R Shaykhutdinova, Gulsara A Slashcheva, et al (2021) Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide Recovers Motor Function in SD Rats after Focal Stroke – Molecules, 2021 Aug 26, Volume 26 (Issue 17), Pages 5173.
[10] M Soyka and H B Rothenhaeusler (1998) Opioid detoxification with delta sleep-inducing peptide: results of an open clinical trial – Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 1998 Jun, Volume 18 (Issue 3), Pages 257-8.
[11] I I Mikhaleva, V T Ivanov, L V Onoprienko, et al (2014) Antioxidant and detoxifying activities of analogues of the delta sleep inducing peptide – Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, 29 January 2014, Volume 40, pages 1–8.
[12] M.V. Graf, A.J. Kastin, and G.A. Schoenenberger (1986) Delta sleep-inducing peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats – Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Volume 24, Issue 6, June 1986, Pages 1797-1799.
[13] V I Odin, T V Belikova, E S Pushkova, N A Barr (2004) [Diabetes mellitus in elderly: geroprotective and antidiabetic properties of delta-sleep induced peptide] – Advances in Gerontology, 2004, Volume 15, Pages 101-14.
[14] K P Lesch, E Widerlöv, R Ekman, G Laux, et al (1988) Delta sleep-inducing peptide response to human corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in major depressive disorder. Comparison with CRH-induced corticotropin and cortisol secretion – Biological Psychiatry, 1988 Jun, Volume 24 (Issue 2), Pages 162-72.
Why Choose Direct Peptides France?
Buy DSIP today from Direct Peptides, your trusted source for high-quality DSIP peptides. We offer Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide (DSIP) in 2mg, 5mg, and 10mg vials, as well as peptide stacks, nasal sprays (15ml and 30ml), and pre-mixed peptide pens. Whether for research or investigative use, we provide the exact formulations you need for your studies.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our France Direct Peptides website: https://direct-peptides.com is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.
Related Posts

Can Sleep Peptides Be An Alternative Treatment For Insomnia?
This article explores sleep peptides like DSIP, CJC-1295, and GHRP-6, which may improve sleep by influencing neurotransmitters, growth hormone, and circadian rhythms. It covers their benefits, mechanisms, and uses, showing their potential as a complement to traditional insomnia treatments and a breakthrough in sleep medicine.

DSIP And Epithalon Anti-Aging Benefits
This article explores the anti-aging potential of the DSIP and Epithalon peptide stack. DSIP supports sleep regulation and endocrine health, while Epithalon activates telomerase to promote cellular rejuvenation. Together, they offer a synergistic approach to combating age-related decline, with promising research suggesting benefits for longevity and quality of life.
Exploring Intranasal Peptides: Efficacy And Applications
This article explores the use of intranasal peptides as a non-invasive method for delivering therapeutic benefits. Peptides like DSIP, Semax, and Oxytocin show potential in improving cognition, mood, sleep, sexual health, and treating neurodegenerative diseases.